Definition
The cell of all living organisms except various Bacteria & certain algae have definite nucleus in the cytoplasm which always covered by a membrane known as nuclear membrane. All such cells are called as a eukaryotic cells.
The eukaryotic cells are larger than prokaryotic cells. It ranges from 10-100πm. These are true cells occur in animals.
Structure
1. Generally the shape or the structure of eukaryotic cell are round and spherical.
2. It may be variable( i.e, frequently changing the shape ) as in amoeba (or) fixed almost in all plants and animals.
3. In fixed cell types, some other shape have also been observed. These are the shapes of oval cuboidal, cylindrical, flat, elongated & spindle shape.
4. The shape of cell depends mainly on functional adaptations & partly on the surface tension of & viscosity of protoplasm.
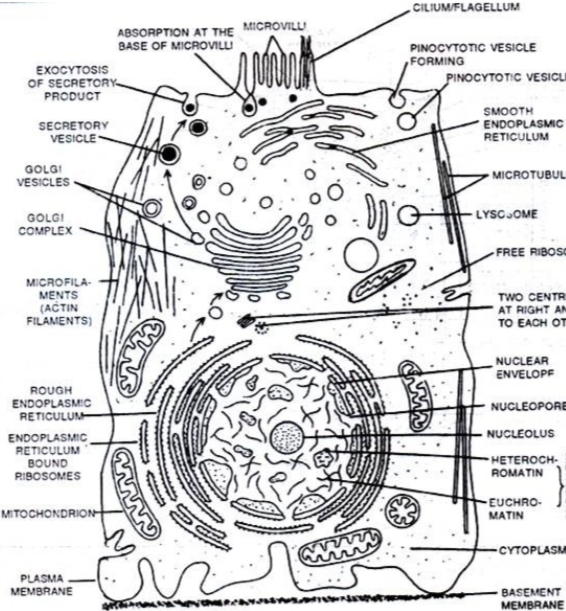
5. The eukaryotic cells are essentially two envelop system.
6. The secondary membrane envelop the nucleus and other internal organelles.
7. The shape, size and physiology may vary in different eukaryotic cells.
Features
– Nuclear envelop is present in eukaryotic cell.
– DNA is combined with proteins.
– Chromosomes are present in multiple and ribosomes are 80’s ( 60’s & 40’s ).
– Cell division is occurs through both the mitosis and meiosis.
– Locomotion is carried out through the cilia in flagella.
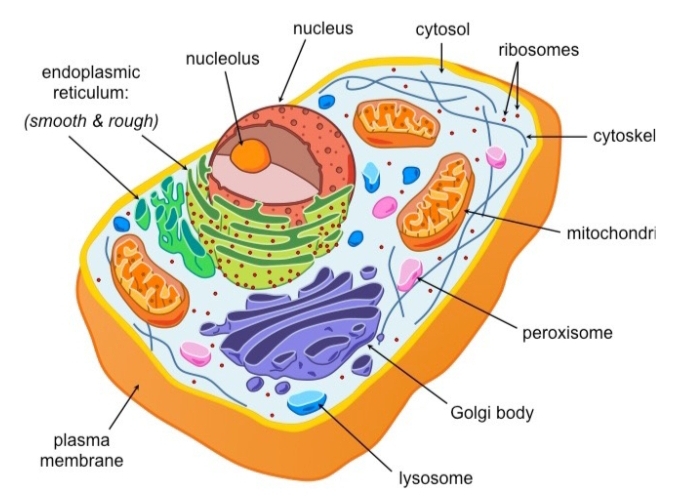
– All eukaryotic cells are composed of plasma membrane, cytoplasm, endo membrane, mitochondria, lysosomes, centrosomes etc., And a true nucleus.
– The eukaryotic cells may be following types,
Epithelial cells, Macrophages, Nerve cells, Bone cells, Brain cells, Ciliated cells, Flagellated cells of connective tissue, Muscle cells, Blood cells, Adipose cells.
Thank you for visiting….