DNA is a polymer of deoxy-ribonucleotides. It is composed of monomeric units namely deoxyadenylate ( DAMP ), deoxyguanylate ( DGMP ), deoxycytidylate ( DCMP ), and deoxythymidylate ( DTMP ).
SYSTEMATIC REPRESENTATION OF POlYNUCLEOTIDES :-
– The Monomeric deoxy nucleotides in DNA are held together by 3′, 5′- phosphodiestes bridges.
– DNA structure is often represented in a short hand form.
– The horizontal line indicates the carbon chain of sugar with base attached to C1. Near the middle of the horizontal line C3 1 phosphate linkage while at the other end of the line is C5 phosphate linkage.
DNA Double Helix
– The double helical structure of DNA was proposed by James Waston and Francis Crick in 1953.
– The structure of DNA Double Helix is composed to a twisted ladder.
Salient Features Of Waston-Crick Model Of DNA :-
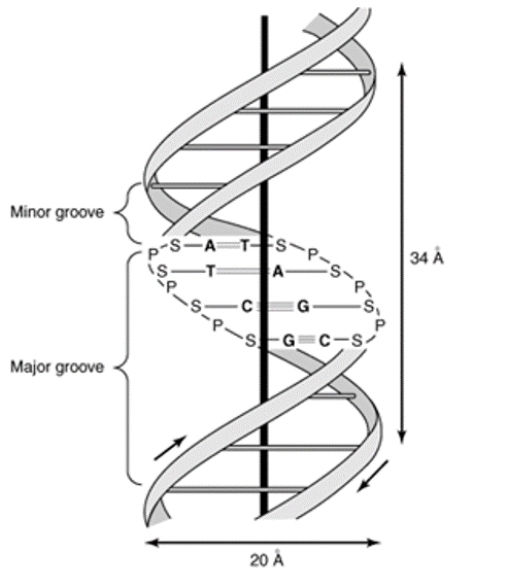
1. The DNA is a right handed double helix. It connect of two polydeoxy ribonucleotide chains twisted around each other on a common axis.
2. The two strands are anti parallel i.e, one strand in the 5′ to 3′ direction while the other is 3′ to 5′ direction.
3. The width of a double helix is 20A° ( 2nm ).
4. Each turn of the helix is 34A° ( 3.4 nm ) with 10 pairs of nucleotides each pair Placed at a distance of about 3.4A°.
5. The two polynucleotide chains are not identical but complementary to each other due to base pairing.
6. The two strands are held together by hydrogen bonds formed by complementary base pairs.
7. The hydrogen bonds are formed between a purine and a pyrimidene only.
8. The only base arrangement possible in DNA structure from special consideration is A-T, T- A, G-C, & C-G.
9. The complementary base pairing in DNA helix proves chargaff’s rule. The content of adenine equals to that of thymine ( A=T ) and guanine equals to that of cytosine ( G=C ).
10. The genetic information resides on one of the two strands known as template strand (or) sense strand. The opposite strand is antesence strand.
11. The double helix has ( wide ) major groove and ( narrow ) minor groove along the phospho di ester back bone proteins interact with DNA at these grooves without dicrupting the base pairs and double helix.
Thank you for visiting